Number of longest increasing subsequences
My favorite problems are those which seem simple but exhibit unexpected depth. A prime example is the Traveling Salesperson Problem: It is simple to understand that the garbage truck needs to collect every garbage container, while trying to take the shortest route.
But here, I want to talk about the problem of the longest increasing subsequence (LIS): For a given sequence of numbers, find the subsequence consisting of increasing numbers, which is longest.
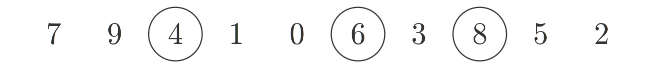
This problem is so simple that it was first studied almost as a placeholder by Stanisław Ulam in a book chapter describing the Monte Carlo method. And judging by the google results, it seems to be a common problem posed to university students. I am wondering how many job applicants were distressed when trying to solve it in front of a whiteboard.

However, apparently one can write whole books about this problem. It turns out that there are
surprising connections to seemingly independent problems. For example, the length
The solution of this problem is not unique: A Sequence can contain multiple longest increasing subsequences. Indeed, their number grows exponentially with the length of the original sequence.

In the end there are
fn lis_len<T: Ord>(seq: &[T]) -> usize {
let mut stacks = Vec::new();
for i in seq {
let pos = stacks.binary_search(&i)
.err()
.expect("Encountered non-unique element in sequence!");
if pos == stacks.len() {
stacks.push(i);
} else {
stacks[pos] = i;
}
}
stacks.len()
}
But we want more, therefore we annotate each card of the rightmost stack with the number of increasing
subsequences of length
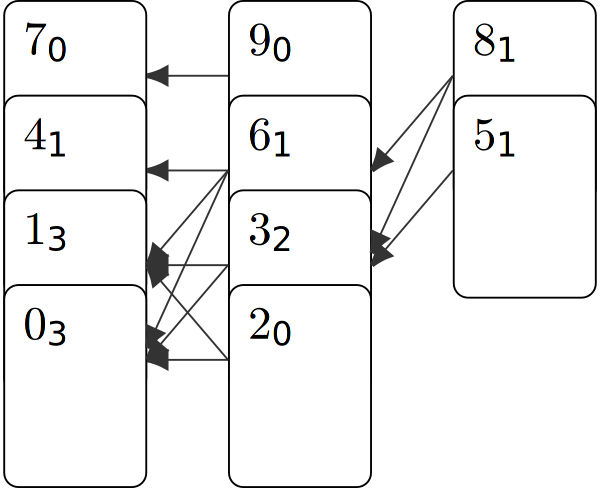
About the behavior for longer sequences from different random ensembles we published an article.